Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
UTIs are very common — particularly for women. Around 1 in 2 women and 1 in 20 men will get a UTI in their lifetime. There are different types of UTIs and this can depend on which part of the urinary tract is infected.
Some people have a higher risk of getting a UTI and some people are more likely to get repeated (recurring) UTIs.
1 in 2 women (50%)
will suffer a UTI in
their lifetime
1 in 20 men
will suffer a UTI in
their lifetime
1 in 4 women
will have a recurrence
within 6 months
What are  ?
?
UTIs are infections that occur in your urinary tract – that’s in your kidneys, bladder or urethra – and are usually caused by bacteria. Different types of UTIs occur depending on which part of the urinary tract is infected:
Parts of the urinary tract include the:
Urethra – the tube through which urine travels from the bladder to the outside of the body.
Bladder – Most urinary tract infections involve the bladder. This occurs when bacteria travel up the urethra into the bladder. The bladder lining becomes inflamed and swollen, it can become painful to pass urine and when you do it may be cloudy or bloody.
Kidneys – remove waste and extra fluid from your blood to make urine.
Ureters – carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder
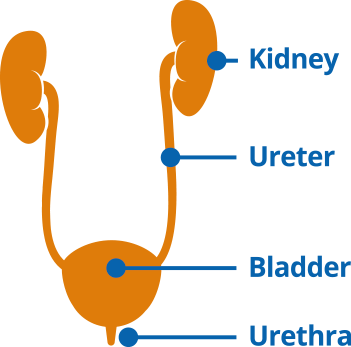
The Urinary Tract
Urinary tract infection 
UTI symptoms can be mild or severe — when
you have a UTI you may notice some or all of
the following common symptoms:
- A burning pain or sensation when urinating
- Wanting to urinate more frequently than normal
– with not much coming out when you do - Feeling like your bladder is still full after
passing urine - Pain in your lower abdomen above the
pubic bone - Cloudy, bloody or smelly urine.
Talk to your health professional if you think you may have a UTI

What causes  ?
?
As the name suggests, UTIs are usually caused by a bacterial infection – with the most common culprit being the bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli). This bacteria is found in the digestive system (and consequently in faeces or poo). It can easily be transferred from the outside of your body into the urethra. From here the bacteria begins to travel up the urinary tract and into the bladder, sticking to the lining as they multiply and cause an infection.
There are also other types of micro-organisms that can sometimes cause UTIs in both men and women. Talk to your Doctor or Pharmacist if you have further questions about managing a UTI.